Introduction
Tribulus terrestris L. is a plant of the Zygophyllaceae family present in many places around the world but mainly cultivated in India, China, Africa and Europe. It is an important plant species in Ayurvedic medicine. The plant and in particular the fruits are reputed to be rich in saponins, moreover the dry fruit extracts are often titrated at 20% or at 40% in saponins. In this context, Tribulus extracts can help optimize natural testosterone levels, sperm count and motility, muscle growth and body strength. They can also increase libido and erectile function. Like all dry extracts, Tribulus Terrestris can be falsified. Let see what are the adulterations that can be encountered on the market.
Study
Issues on the dry herbs
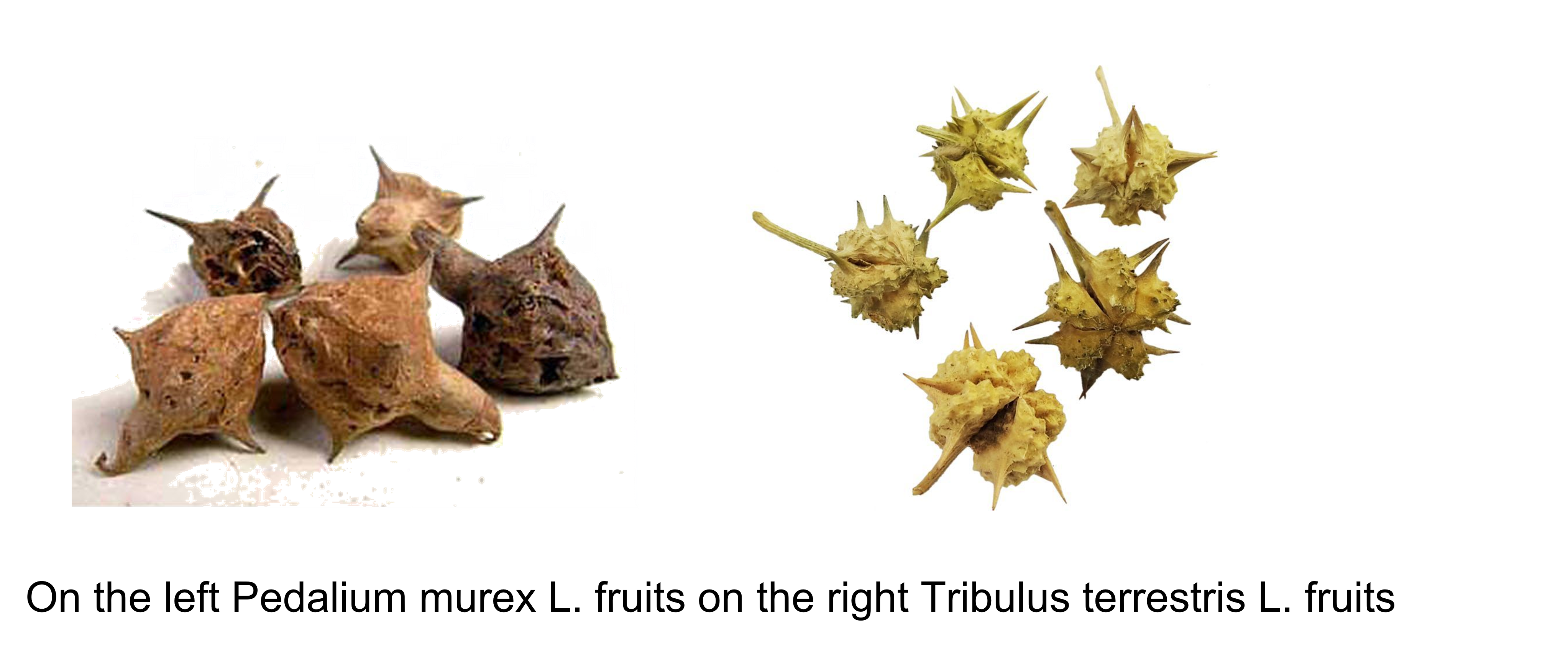
In the case of Tribulus, there can be confusions (involuntary) as well as falsifications (voluntary). Dried fruits can be confused with the species Pedalium murex L., another plant of Ayurvedic medicine. When the fruits are purchased in Asia, this risk of confusion is greater because the species P. murex is also used for the treatment of sexual disorders. Even if the eye of a neophyte can easily make the distinction, this confusion is nevertheless found on the market and in particular among herbalists which trigger issue to the rest of the production chain of the extract. The analyses carried out to identify and differentiate the species are often very basic. These analyzes are generally based on the presence of saponins which are known to be the active ingredients responsible for the activity, but both species contain them. Moreover, these saponin assays are often carried out by gravimetry for the vast majority of samples on the market. Bear in mind that an analysis by gravimetry is absolutely not specific and can include molecules from totally different families in the result.
Relying solely on the presence of saponins is therefore not sufficient to identify Tribulus. These values of saponins obtained by gravimetry are problematic because the extracts of Tribulus titrated to 20% or 40% of saponins are far from containing this concentration. In reality, saponins are often present in small quantities and some of these extracts contain only traces of saponins. Gravimetric methods artificially overestimate saponin assay results. Don’t be fooled and check the titers by reliable methods like HPLC.

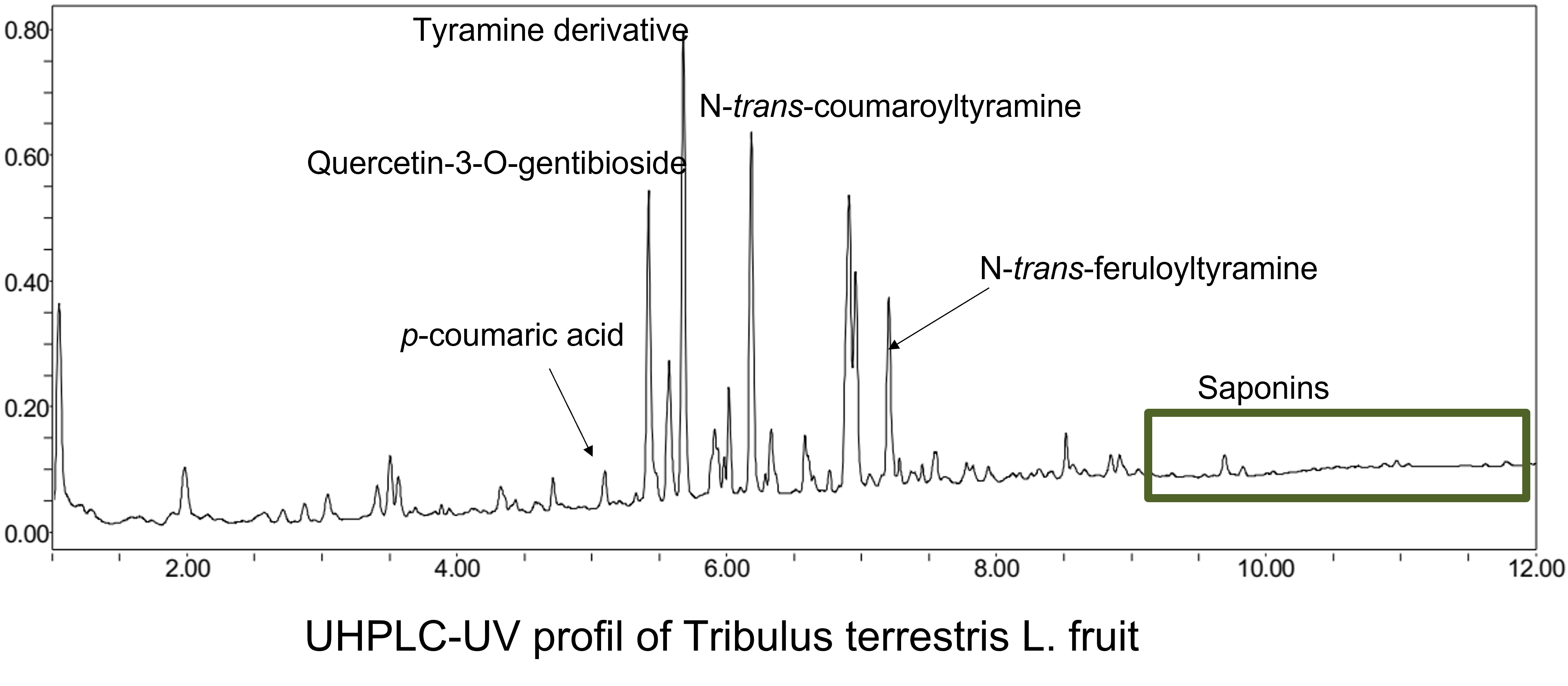
Issues on the extracts
The examples of fraud/falsification seen above are valid on dry extracts for lack of identification of the dry herb but we can face other one. We´ve recently faced many commercial samples supposed to be only from the fruits of Tribulus terrestris L. mixed with Fenugreek extracts. Why ? Once again the problem of the analysis of saponins. Fenugreek extracts are often highly titrated in saponins (sometimes 50%). The contents are generally obtained by gravimetry. As said previously, this technique considerably boosts the levels found and is not at all specific. Thus, if the authentication of the dry extract is carried out based only on the only based on the content of saponins obtained by gravimetry there will be no possibility of differentiating the saponins of Tribulus from the saponins of Fenugreek.
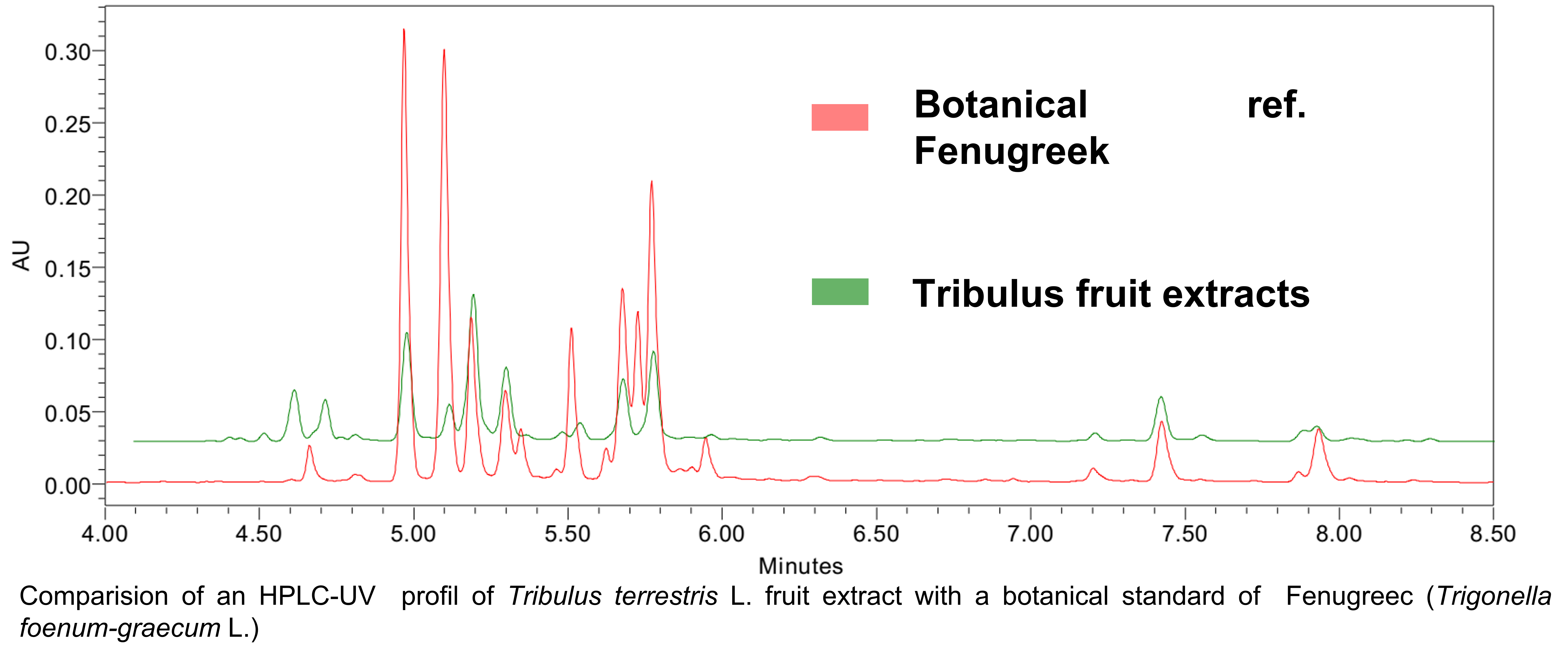
However, the distinction between the two species is easy based on the total chemical composition. In the present case, it is easy to see that the profile of the commercial dry extract of Tribulus fruit is very similar to the profile of the reference Fenugreek compared. In the current context, with so many plant species on the market we face an increasingly number of frauds.
Methods as irrelevant as dosages by gravimetry or by UV spectrophotometry should no longer be used because they bring more confusion on the market.
Conclusion
Carrying out an unsuitable control (here with the gravimetric assay) can prove to be worst than not carrying out a control at all.
How to ensure the quality of your Tribulus samples?
By proving the presence of Tribulus, the absence of other plant species, the absence of enrichment and by verifying the quantities of claimed active ingredients with appropriate methods.

