Introduction
Since January 2015, lots of European countries ask to monitor some actives in botanical extracts to be sold in the market. For example, in France, for Valeriana officinalis and Valeriana jatamansis it is necessary to:
• prove the absence of valepotriates (with a detection limit)
• monitor valerenic acid levels
• identify these plants via the presence of relevant markers
To guarantee the safety of marketed products, one of the great difficulties is to propose reliable methods allowing the identification of specific markers (with inter-species differentiation) and the dosage of molecules belonging to the valepotriate family.es valépotriates.
Analysis
BOTANICERT has implemented specific study protocols on the topic of valerian:
• A screening method with specific and relevant chemotaxonomic markers
• A method developed for the qualification and dosage of valepotriates
• A method to allow the reliable identification of markers specific to the genus Valerianae spp
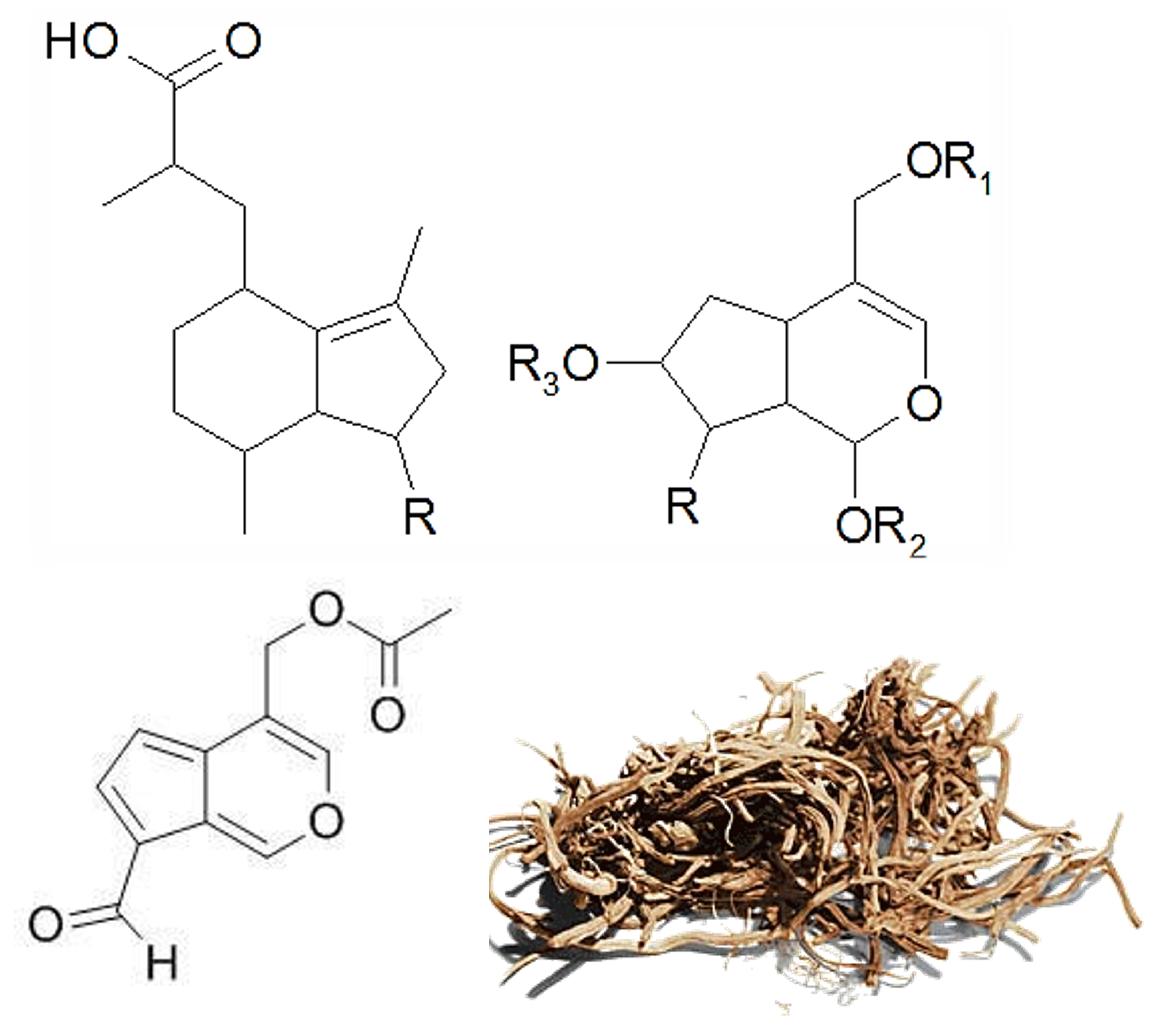
In the picture : Top left, basic structure of a valerenic acid, top right, basic structure of a valepotriate and bottom, structure of baldrinal (degradation product of valepotriates)
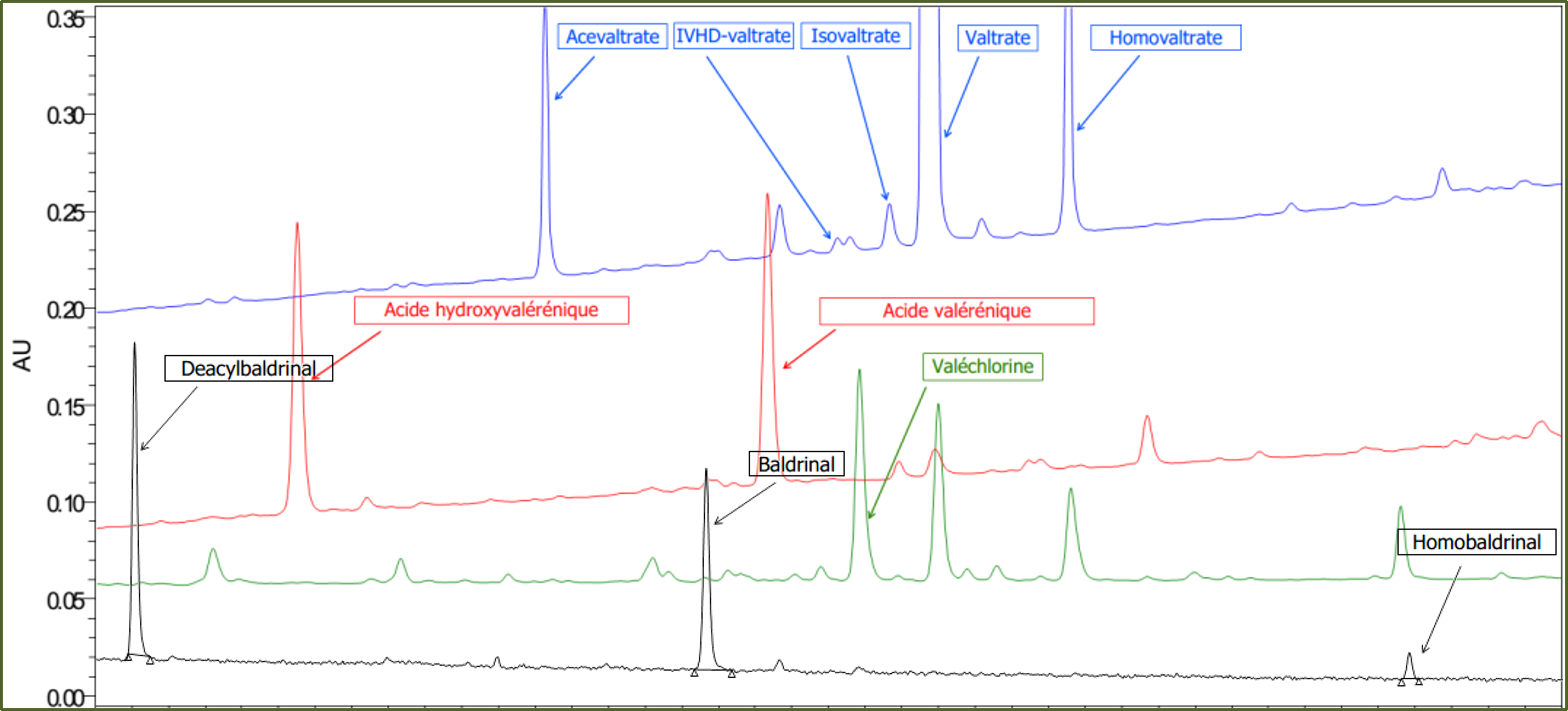
Screening method using chemotaxonomic markers of the species
Identification of the following chemotaxonomic markers: Valtrate, Isovaltrate, Acevaltrate, IVHD-valtrate, Valechlorine, Homovaltrate, Baldrinal, Deacylbaldrinal, Homobaldrinal, Valerenic Acid, Hydroxyvalerenic Acid
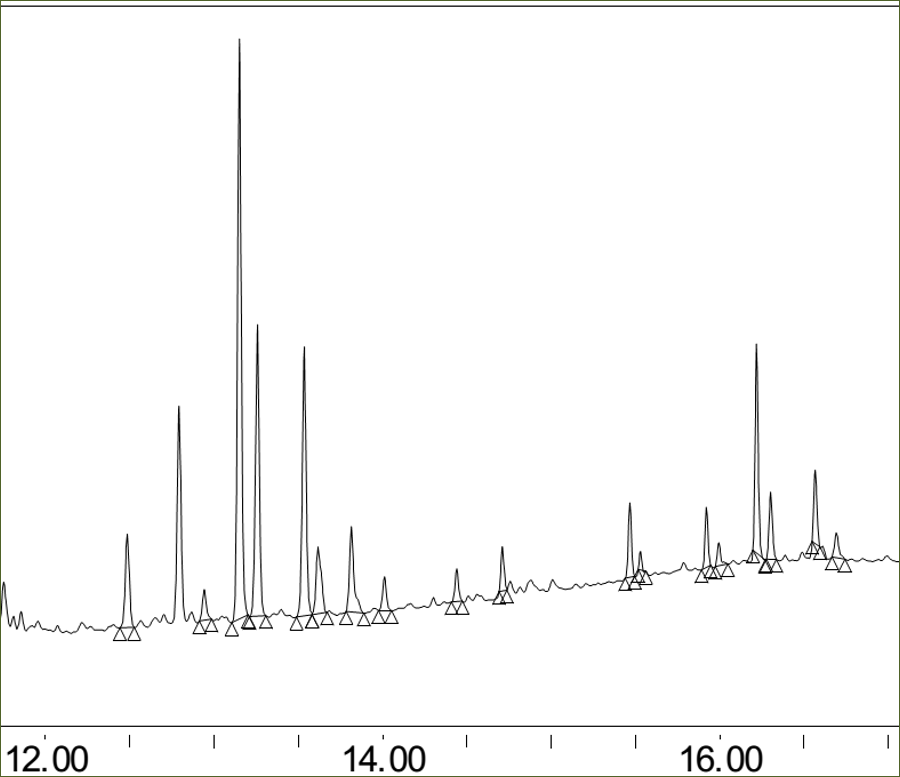
Valepotriate assay method
Identification of the valepotriate family on a control sample. This control sample is then used to dose the valepotriates with valtrate as an equivalent.
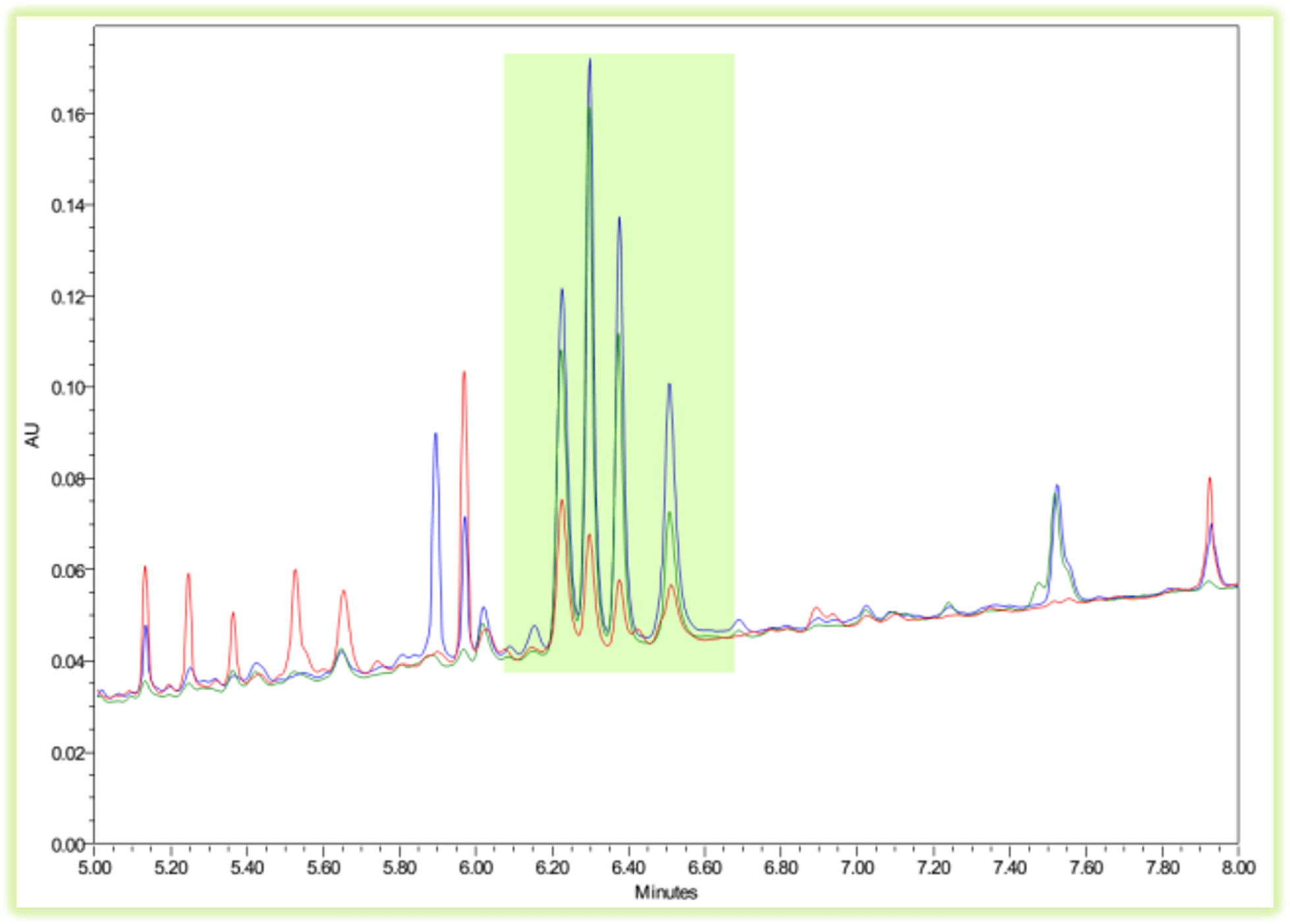
Genus markers Valerianae spp
A motif of 4 characteristic substances has been identified in different species of the genus Valerianae. This motif, denoted VAL601, has not been found in other related species of the genus Valerianae.In addition to the valtrate / isovaltrate ratios, presence of valerenic acids and valepotriates, this pattern makes it possible to add a criterion of differentiation on the fingerprints of the genus Valerianae.
Conclusion
How can you be sure of the quality of your plant-based raw materials?
Control the identity of the raw material (botanical and phytochemical identification) as well as its quality (assay of markers of interest / chemotaxonomic).
For the example of valerian:
• Botanical identification (microscopy)
• Phytochemical identification (HPTLC/UHPLC)
• Relevant dosage of markers of interest (valepotriates / valerenic acids)
• Sale of a botanical standard of Valerian

